Human growth hormone (hGH) is a naturally occurring peptide or protein hormone secreted by the pituitary gland. Growth hormone (GH or HGH) is also known as somatotropin or somatropin. It is a peptide or protein hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction and regeneration in humans. In the body the hormone is rather heterogeneous. The major isoform of the human growth hormone is a protein of 191 amino acids and a molecular weight of 22,124 daltons.
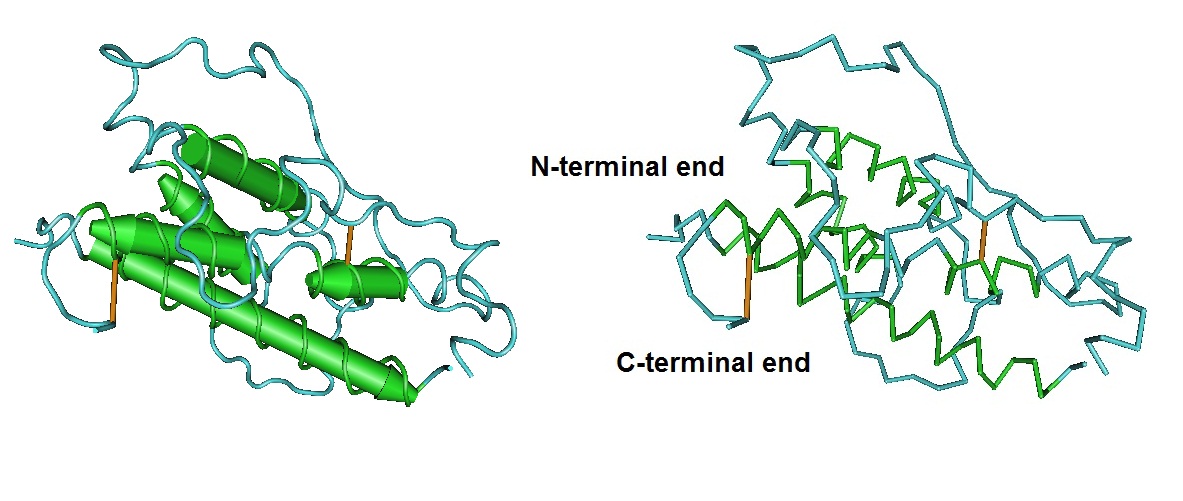
 3D models of HGH {Source PDB: 1HGU}
3D models of HGH {Source PDB: 1HGU}
The three-dimensional structure is stabilized by two disulfide bridges four helical structures. The position of the helices and the overall three-dimensional structure of this hormone are important for receptor binding. The hormone shares structural homologies with prolactin and human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS). HCS is a growth hormone variant synthesized exclusively in the placenta. There is a cluster of five genes from which these polypeptide hormones may be synthesized but normally only one gene expressed tissue-specifically. Binding of the tissue-specific transcription factor Pit-1 to the promoter region of the growth hormone gene results in only one form of growth hormone that are secreted by the anterior pituitary gland.
Before recombinant technology was available, the only source of hGH was human cadavers, but the contamination that led to Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease made this form of treatment obsolete. During the late 1980s, recombinant hGH (rhGH) was developed through genetic engineering. Recombinant hGH has been used with good results in the treatment of patients with hGH deficiency allowing bone growth and impacting on the patient’s final stature. This form of hGH has a sequence identical to the naturally occurring 22 kDa hormone.
Some athletes and bodybuilders appear to have used rhGH and claim that it increases lean body mass and decreases fat mass. Besides its anabolic properties hGH also effects carbohydrate and fat metabolism. During sport doping investigations rhGH has been found in swimmers and also in players taking part in other major sports events. International federations and the International Olympic Committee have hGH now on the list of forbidden compounds since 1989.
Human growth hormone is secreted from somatotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland in a pulsating fashion. Two hypothalamic peptides, growth hormone releasing hormone, which stimulates hGH secretion, and somatostatin, which inhibits hGH secretion by back regulation, regulate its secretion.
hGH binds to specific receptors present throughout the whole body and exerts its biological effects on target cells. The secretion of hGH is slightly higher in women than in men. The highest levels are observed at puberty. Secretion decreases with age by approximatelly 14 % per decade. In addition, secretion of the hormone varies with normal physiological and pathological conditions and hGH levels are higher during slow wave sleep and are increased by exercise, stress, fever, fasting and, with increased levels of some amino acids (leucine and arginine). Drugs, such as clonidine, L-dopa and c-hydroxybutyrate, increase its secretion, as do androgens and estrogens. hGH binds to specific membrane receptors found in abundance throughout the body. It has both direct and indirect effects on the tissues. Indirect effects are mediated by IGF-1, generated in the liver in response to GH.
"GH1 growth hormone 1 [ Homo sapiens (human) ]: The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin family of hormones which play an important role in growth control. The gene, along with four other related genes, is located at the growth hormone locus on chromosome 17 where they are interspersed in the same transcriptional orientation; an arrangement which is thought to have evolved by a series of gene duplications. The five genes share a remarkably high degree of sequence identity. Alternative splicing generates additional isoforms of each of the five growth hormones, leading to further diversity and potential for specialization. This particular family member is expressed in the pituitary but not in placental tissue as is the case for the other four genes in the growth hormone locus. Mutations in or deletions of the gene lead to growth hormone deficiency and short stature. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]"{Source: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/2688}
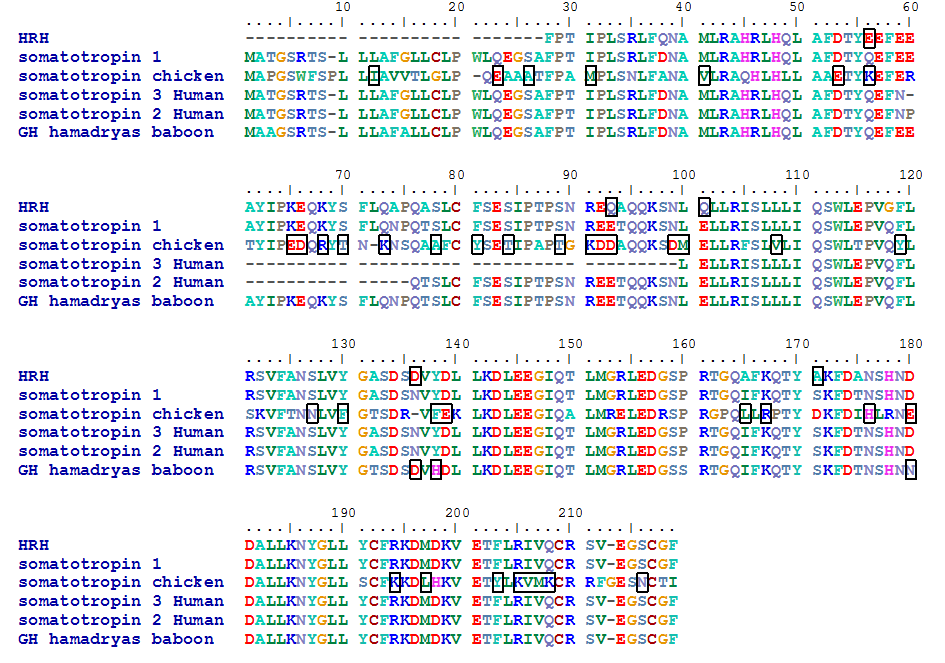 Figure 1: Alignment of the sequence of human growth hormone with various somatotropin sequences.
Figure 1: Alignment of the sequence of human growth hormone with various somatotropin sequences.
Growth hormone belongs to the somatotropin family, a protein family whose major representative is somatotropin. Somatotropin is also known as growth hormone. The hormone plays an important role in growth control. Other members of this family include choriomammotropin (lactogen), prolactin, placental prolactin-related proteins, proliferin and proliferin related protein, as well as somatolactin from various fishes.
References
Chantalat L, Jones ND, Korber F, Navaza J, Pavlovsky AG; The crystal-structure of wild-type growth-hormone at 2.5 angstrom resolution. Protein Pept.Lett. (1995) 2 p.333.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/2688
M Saugy, N Robinson, C Saudan, N Baume, L Avois, P Mangin; Human growth hormone doping in sport. Br J Sports Med 2006;40(Suppl I):i35–i39. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2006.027573.