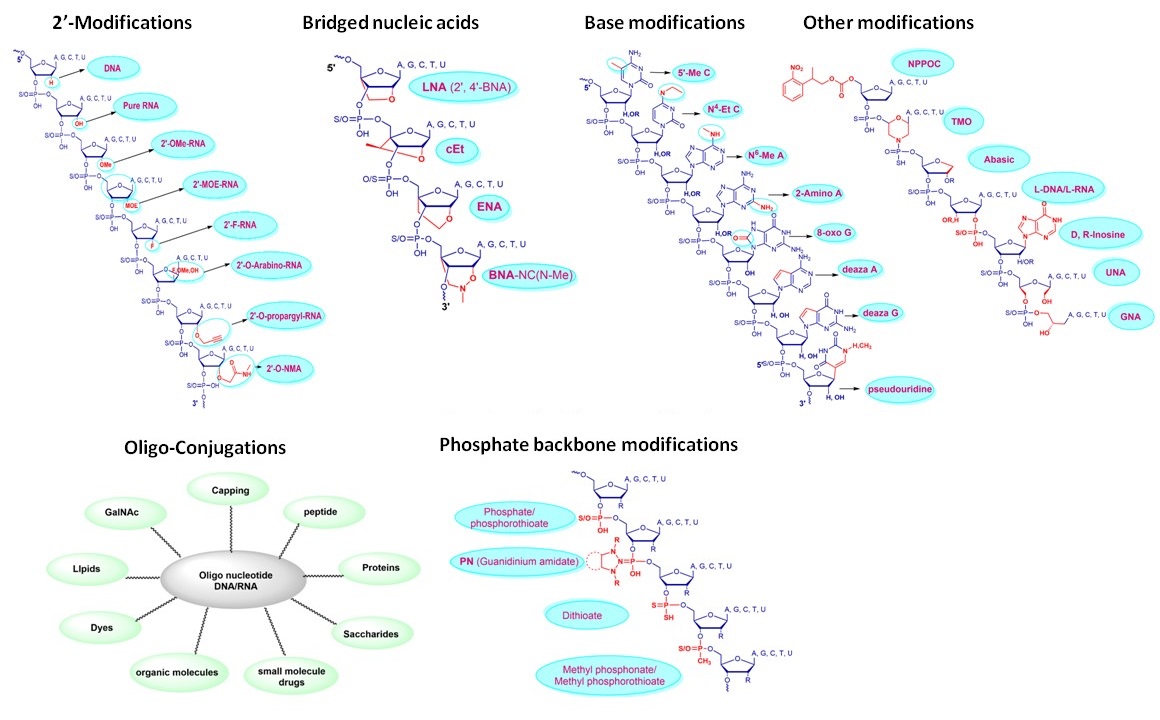
Discover the power of oligonucleotide modifications!
These incredible molecular tweaks can transform ordinary oligonucleotides into potent antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), splice-switching oligonucleotides (SSOs), small interfering RNA (siRNA), and RNA aptamers. Unleash the full potential of your research and explore the possibilities with oligonucleotide modifications.
Therapeutic oligonucleotides are short DNA/RNA-like strands that utilize gene-silencing techniques for various applications. These short DNA/RNA oligonucleotides can regulate gene expression by binding to target mRNA sequences via Watson-Crick base pairing through hydrogen bonds. Their specific binding ability to the complementary mRNA makes them a potential tool for drug development, as they can selectively target undruggable human and viral genomes. Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are the two most used gene silencing strategies.
Antisense oligonucleotides (ASO), function as a single strand. Their mechanism of action involves either promoting RNA degradation through the RNase H enzyme or without degradation through splice modulation and translation arrest. Targeting specific codons, splicing modulators prevent splicing during translation through exon skipping and inclusion. Pre-mRNA splicing machinery binds to ASOs to skip mutant exons, repair RNA frame, and produce functional proteins in exon skipping. ASOs attach to pre-mRNA to prevent splicing machinery from accessing transcript sites, resulting in exon exclusion. Splice-modulating oligonucleotides can treat disorders with splicing defects or disease-causing mutations in target exons. Steric blocker oligonucleotides bind to target RNA and inhibit ribosomal activity, causing translational arrest through steric hindrance. Gene expression inhibitors cause selective breakdown of DNA-RNA heteroduplexes via RNase H enzyme, releasing mRNA and leaving DNA intact, reducing target gene translation.
Small interfering RNAs, commonly known as siRNAs, are double-stranded oligonucleotides consisting of a guide strand and a passenger strand. RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which double-stranded small interfering RNAs (siRNA) induce mRNA degradation and suppress target gene expression. During RNA interference (RNAi), a small RNA duplex combines with the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The passenger strand is discarded, and the remaining guide strand works with RISC to bind complementary RNA sequences.
Most widely used modifications of oligonucleotides