Viroids are plant infecting particles smaller than a virus containing nucleic acids without a protein coat. Viroids genomes are naked small single-stranded circles of RNA. This single-stranded circular RNA (circRNA) molecule can vary in length from 246 to 463 nucleotides and is the smallest pathogens found so far. The unique properties of viroids allow them to infect plant cells without encoding for any protein without resorting to a helper virus.
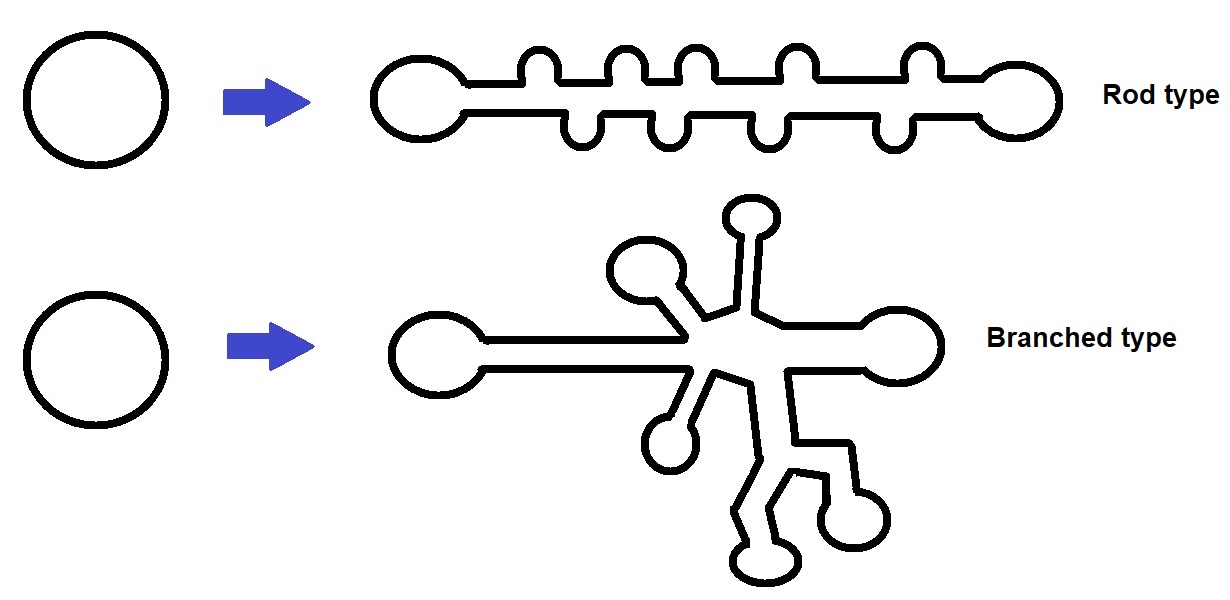
Figure 1: Viroid RNA can form circular, rod type and branched strutures. Some just form simple rod-like structures, whereas others have complex branched structures.
Viroids can infect plants and cause certain diseases. In the infected plant, RNA replication occurs at the expense of the host cell. Since viroids lack proteins for attachment to host membranes, they can only infect plant cells that are already damaged. Inside plant cells, they may be passed from one plant cell to another via cellular junctions.
Members of the two viroid families, Pospiviroidae and Avsunviroidae, replicate through a rolling-circle mechanism involving RNA polymerization, cleavage, and ligation. For replication in a plant cell, viroids must enter the nucleus.
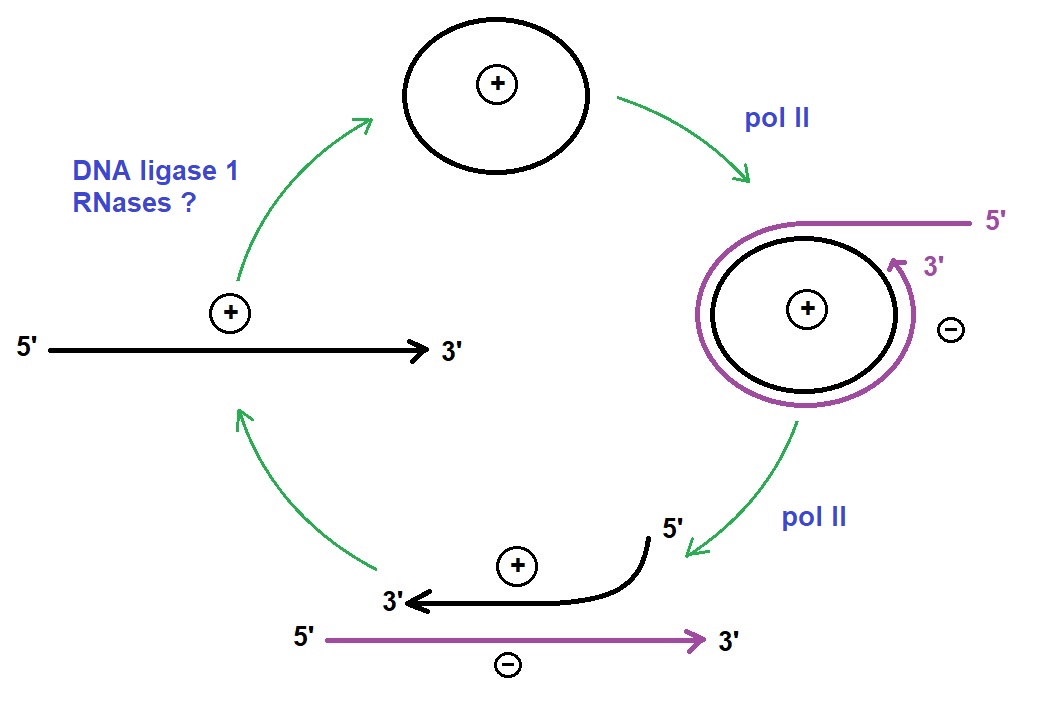
Figure 2: Replication cycle of viroids. Pospiviroidae replicates in an asymmetric cycle. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (pol II) transcribes mature circular RNA into oligomeric (-) intermediates. Next, (-) intermediates are converted into oligomeric (+) intermediates. DNA ligase 1 cleaves the (+) intermediates into monomers and ligates them into mature circles. (Adapted from Clark; Molecular Biology).
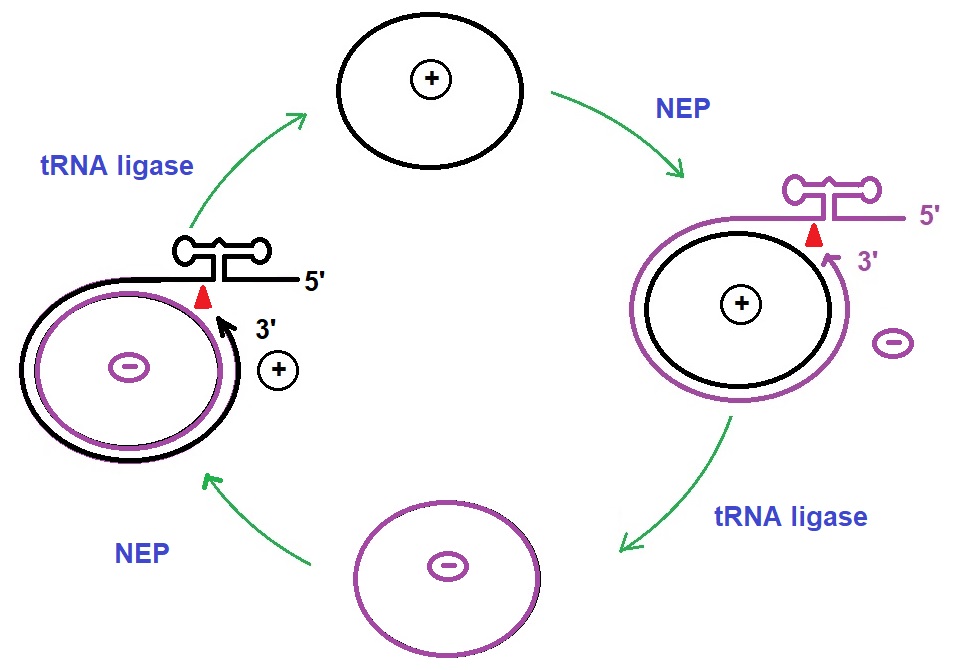
Figure 3: Replication cycle of viroids. Avsunviroidae replicates in a symmetrical cycle. Circular RNA is transcribed into oligomeric intermediates by the nucleolar-encoded polymerase (NEB) and is cleaved into monomeric units by the hammerhead ribozyme followed by ligation into cycles by tRNA ligase. circRNA can fold into thermodynamically stable and metastable structures whose presence is critical for each step of the different replication cycles (Steger & Riesner 2018. Adapted from Clark; Molecular Biology).
Synthetic viriods allow the study of RNA transport in plant tissue. Viroids can move intracellularly, intercellularly through plasmodesma, and other parts through the vascular system. Viroids can act as silencing molecules, and some have catalytic functions.
For example, the potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVd) infects tobacco plants where it can trigger RNA-directed DNA methylation of homologous sequences resulting in gene silencing. Viroids are also able to induce post-transcriptional gene silencing via viroid-derived small RNAs.
Viroids are part of a circRNA pool now recognized as a large RNA class with a longer half-life than linearized RNAs which may act as miRNA sponges and are involved in gene expression and splicing.
Daros et al., in 2018, showed that the expression of Eggplant latent viroid (ELVd) derived RNAs in Escherichia coli together with the eggplant tRNA ligase allow the production of RNAs of interest like aptamers, extended hairpins, or other structured RNAs in amounts of tens of milligrams per liter of culture. tRNA ligase is the enzyme involved in viroid circularization in the infected plant.
Viroids can infect many woody plants and herbs, and several viroid-induced plant diseases are of considerable economic importance. For example, infection of potatoes with PSTVd can result in significant losses. Other examples are the infection of Chrysanthemum with Chrysanthemum stunt viroid (CSV), citrus plants with Citrus exocortis viroid (CEVd), coconut palms with Coconut cadang-cadang viroid (CCCVd), and avocado with Avocado sunblotch viroid (ASBVd).
Therefore, the exclusion or eradication of infected materials is the most effective means of controlling viroid diseases. However, routine diagnosis of viroid diseases based on symptom expression in their natural hosts is often tricky. See Hammond & Owens for more detail.
Labeled cRNA probes allow viroid detection via dot blot hybridization protocols, for example, by utilizing digoxigenin-labeled probes or via 32P-based autoradiography.
Seo et al., in 2020, showed that the time for half-maximal nuclear accumulation of the fluorescently labeled potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVd) was about 23 min. To find out, the research group microinjected leaves of tobacco plants (N. benthamiana) with Alexa Fluor 488 or Alexa Fluor 546 labeled PSTVd-intermediates and used fluorescence microscopy to observe the accumulation of the viroids in plant compartments and their import into the plant nucleus.
Reference
David P. Clark, Molecular Biology 3rd Edition.
Daròs JA, Elena SF, Flores R. Viroids: an Ariadne's thread into the RNA labyrinth. EMBO Rep. 2006 Jun;7(6):593-8. [PMC]
Daròs, JA., Aragonés, V. & Cordero, T. A viroid-derived system to produce large amounts of recombinant RNA in Escherichia coli. Sci Rep 8, 1904 (2018).[Nature]
Rosemarie W. Hammond and Robert A. 2006. Viroids: New and Continuing Risks for Horticultural and Agricultural Crops. Oniine. APSnet Features. doi: 10.1094/APSnetFeature-2006-1106. [Link to The American Phytopathological Society (APS) info]
Podleckis EV, Hammond RW, Hurtt SS, Hadidi A. Chemiluminescent detection of potato and pome fruit viroids by digoxigenin-labeled dot blot and tissue blot hybridization. J Virol Methods. 1993 Jul;43(2):147-58. [PubMed]
Steger G, Riesner D. Viroid research and its significance for RNA technology and basic biochemistry. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Nov 16;46(20):10563-10576. [PMC]
Seo H, Wang Y, Park WJ. Time-Resolved Observation of the Destination of Microinjected Potato Spindle Tuber Viroid (PSTVd) in the Abaxial Leaf Epidermal Cells of Nicotiana benthamiana. Microorganisms. 2020 Dec 20;8(12):2044. [PMC]
Viroids